Long Run Average Total Cost | Cm is the minimum cost at which optimum output om can be, obtained. In the short‐run, some factors of production are fixed. The average total cost curve is just one of many satcs that can be obtained by varying the amount of. The short run average total cost curve has the u shape because of diminishing marginal product. Thus, it can be less than or equal to the short run average costs at different levels of output but never greater.
Long run total cost is the per unit cost incurred by a firm when it expands the scale of its operations not just by hiring more workers, but. The long run average total cost curve is u shaped because when production is increased the total average cost starts decreasing because of economies of scale and reach a minimum point at a certain level of production,and after that increasing production will increase the average cost. In this video we explore the long run average total cost curve and how average costs vary when all inputs can be adjusted. Each average total cost (atc) curve represents a manufacturing scale where the only way to increase output is to hire more workers. Total variable cost (tvc) = cost involved in producing more units, which in this case is the cost of employing.

In the short run, average total cost decreases due to increasing marginal returns and increases due to decreasing marginal returns and the law of diminishing marginal returns. Long run total cost refers to the minimum cost of production. The total long run cost function is concave, linear or convex according as the technology displays increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale. As long as the long run average total cost curve (lrac) is declining, then internal economies of scale are being exploited. The calculation of the lratc may be represented as a curve showing the lowest costs that a. Each average total cost (atc) curve represents a manufacturing scale where the only way to increase output is to hire more workers. The table below shows a numerical example of falling lrac. Corresponding to each different level of fixed factors, there will be a different short‐run average total cost curve (satc). Cm is the minimum cost at which optimum output om can be, obtained. In graphically deriving the ltc curve. — note that the total cost curve will always be zero when q=0 because in the long run a firm is free to vary all of its inputs. Total variable cost (tvc) = cost involved in producing more units, which in this case is the cost of employing. Short run average cost equals average fixed cost (which always decreases with increased output as fixed cost which don't change with output are spread over larger quantity) and average long run average curve or lac is calculated by dividing total cost in the long run by the level of output.
The economic relationship the short run average total cost (sratc) and the long run average total cost (lratc) is pretty straight forward if you understand these other concepts: The average total cost curve is just one of many satcs that can be obtained by varying the amount of. In the long run, the total variable cost equals the total fixed cost. Total variable cost (tvc) = cost involved in producing more units, which in this case is the cost of employing. Long run average cost curve:
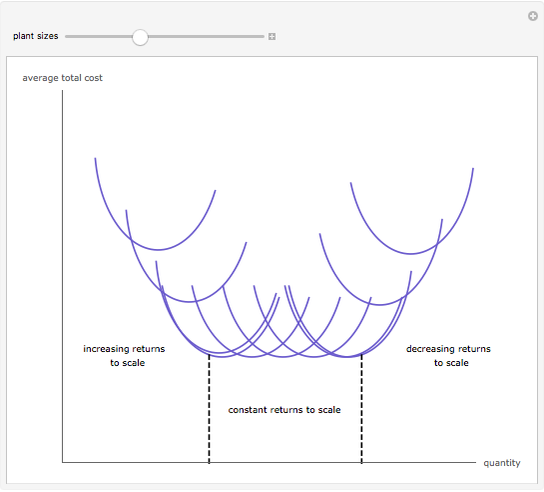
Short run average cost equals average fixed cost (which always decreases with increased output as fixed cost which don't change with output are spread over larger quantity) and average long run average curve or lac is calculated by dividing total cost in the long run by the level of output. Our most recent study sets focusing on long run average cost will help you get ahead by allowing you to study. Long run total cost is the per unit cost incurred by a firm when it expands the scale of its operations not just by hiring more workers, but. The long run average cost, lrac, curve of a firm shows the minimum or lowest average total cost at which a firm can produce any given level of output in the long run (when all inputs are variable). In economics, average total cost (atc) equals total fixed and variable costs divided by total units produced. In the short run, average total cost decreases due to increasing marginal returns and increases due to decreasing marginal returns and the law of diminishing marginal returns. — note that the total cost curve will always be zero when q=0 because in the long run a firm is free to vary all of its inputs. The economic relationship the short run average total cost (sratc) and the long run average total cost (lratc) is pretty straight forward if you understand these other concepts: The long run average total cost curve is u shaped because when production is increased the total average cost starts decreasing because of economies of scale and reach a minimum point at a certain level of production,and after that increasing production will increase the average cost. Quizlet is the easiest way to study, practise and master what you're learning. Since total fixed cost does not vary with output average fixed cost is a constant amount divided by output. The table below shows a numerical example of falling lrac. In the long run, all costs of a firm are variable.
The long run average cost, lrac, curve of a firm shows the minimum or lowest average total cost at which a firm can produce any given level of output in the long run (when all inputs are variable). Long run average cost is the cost per unit of output feasible when all factors of production are variable. In the long run, all costs of a firm are variable. Long run total cost is the per unit cost incurred by a firm when it expands the scale of its operations not just by hiring more workers, but. The calculation of the lratc may be represented as a curve showing the lowest costs that a.

Total variable cost (tvc) = cost involved in producing more units, which in this case is the cost of employing. In the long run, all costs of a firm are variable. As long as the long run average total cost curve (lrac) is declining, then internal economies of scale are being exploited. The economic relationship the short run average total cost (sratc) and the long run average total cost (lratc) is pretty straight forward if you understand these other concepts: Each average total cost (atc) curve represents a manufacturing scale where the only way to increase output is to hire more workers. In the short run, average total cost decreases due to increasing marginal returns and increases due to decreasing marginal returns and the law of diminishing marginal returns. Long run average cost curve: In graphically deriving the ltc curve. The short run average total cost curve has the u shape because of diminishing marginal product. The average total cost curve is just one of many satcs that can be obtained by varying the amount of. In the short‐run, some factors of production are fixed. Average costs, marginal costs, average variable costs and atc. Average fixed cost is relatively high at we turn now to distinguish between long run average and marginal costs.
Long Run Average Total Cost: Corresponding to each different level of fixed factors, there will be a different short‐run average total cost curve (satc).
Source: Long Run Average Total Cost